Maximize Cost Efficiency in Data Transfer
By Khushi Carpenter, Piyush Jalan / May 22, 2024
Table of Contents
Introduction
Nowadays, many individuals and businesses opt for public cloud providers over on-premises solutions to cut down on infrastructure and operational expenses. However, upon reviewing the bills, it becomes clear that the costs can be quite high. To address this issue, the field of FinOps offers opportunities for savings. One area where costs can be reduced is data transfer expenses. In this is blog, we will explore the basics of data transfer costs, its several types, how AWS charges for data transfers and ways to cut down on expenses.
Data Transfer Charges
AWS Data transfer charges refer to the fees that AWS applies for the movement of data either between AWS and the Internet or between AWS services such as EC2 and S3. These charges are divided into two categories:
- Data transfer in: It involves charges for uploading data to the cloud. It is also known as inbound charges and is free. For example, uploading the images from your local drive to S3 bucket via Internet.
- Data transfer out: It involves charges for downloading data from the cloud, It is also known as outbound charges. For example, downloading images stored in a S3 bucket. to local computer.
You can locate data transfer and bandwidth charges in your AWS bill, with data transfer charges pertaining to charges within AWS and bandwidth charges referring to transfer charges with the Internet. Typically, data transfer charges are calculated by the GB.
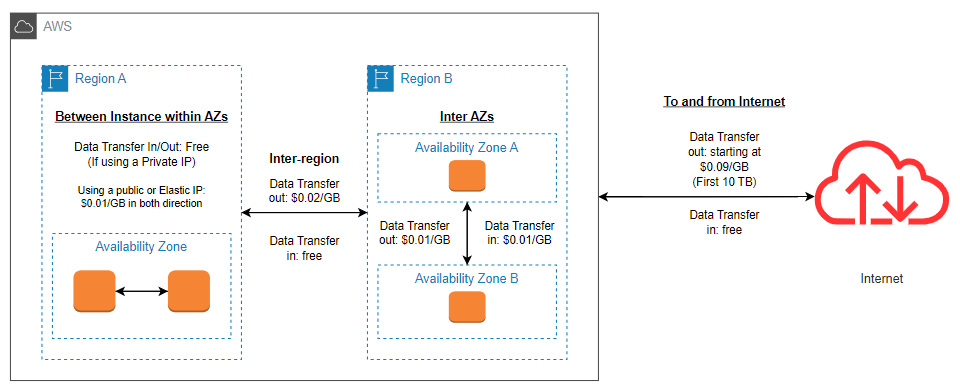
When it comes to AWS Data Transfer pricing, there are a few things to consider.
- The cost of data transfer will depend on whether the data stays within the AWS Cloud or goes out to the public Internet.
- The specific AWS region you are operating in will also affect the price of data transfer.
- Each region has different charges for incoming and outgoing data transfers.
- Transferring data between different regions will be more expensive than keeping it within the same region.
- Transferring data between different Availability Zones will be more expensive than keeping it within the same AZ (Availability Zones).
- The data transfer fees only apply to outbound data from an AWS service.
To understand it more clearly consider the following diagram.
Optimise Data Transfer Cost
There are some areas for which we could save cost, and which are:
- Choose region wisely:
When deciding on the location for your workload, it is important to consider the data transfer out or egress costs for each region. In some cases, choosing a region with lower costs can help optimize expenses. Additionally, using a free tier account for the first 100 GB of data transfer out can also be cost-effective. It is important to note that egress costs can vary depending on the region, internet, and specific services used. To ensure you are choosing the most cost-effective option, refer to the pricing table for data transfer out from regions to all other regions.
For example, the egress cost for us-east-2(Ohio) to all other regions is $0.02 USD per GB while for af-south-1(Cape town) is $0.09 USD per GB. Note that the costs for data transfer out can differ depending on the region, internet, and specific services used. Therefore, it may be beneficial to opt for a region with lower costs to optimize expenses.
Below is the table for pricing of data transfer out from regions to all other regions:DTO to all other regions Price per GB US East (Ohio) $0.02 US East (N. Virginia) $0.02 Asia Pacific (Singapore) $0.09 Asia Pacific (Seoul) $0.08 Asia Pacific (Mumbai) $0.09 Africa (Cape Town) $0.15 Asia Pacific (Hong Kong) $0.09 Asia Pacific (Jakarta) $0.10 Europe (London) $0.02 Israel (Tel Aviv) $0.08 Middle East (Bahrain) $0.11 Middle East (UAE) $0.09 South America (Sao Paulo) $0.14 - Keep data between same regions and AZs:
In situations where it is necessary to duplicate environments for multi-AZ and multi-Region to meet RTO (Recovery Time Objective) and RPO (Recovery Point Objective) requirements, it may be wise to consider cost-saving alternatives. If the workloads are stateless and can be regenerated, replication can be avoided, resulting in significant cost savings. Additionally, when it comes to replicating important workloads across regions and AZs, it is worth considering opting for a cheaper region. Typically, regions in America and Europe are more cost-effective than India, Singapore, and South Africa. - Use public IP addresses prudently:
When it comes to transferring data, it is more cost-effective to use private addresses instead of public addresses. By opting for private addresses, you can significantly reduce expenses and optimize costs when transferring data across AZs. - Make use of Cloud Front:
In the absence of Cloud Front in your architecture, you will be charged for data transfer out for every service that interacts with users over the internet or from different regions. Here is a diagram that provides a more detailed understanding of this.To minimize data transfer costs, it is crucial to use a content delivery network like Amazon CloudFront. This network prioritizes the most frequently accessed content by moving it to the front of the AWS network (known as Points of Presence), ensuring a speedy delivery to your end-users.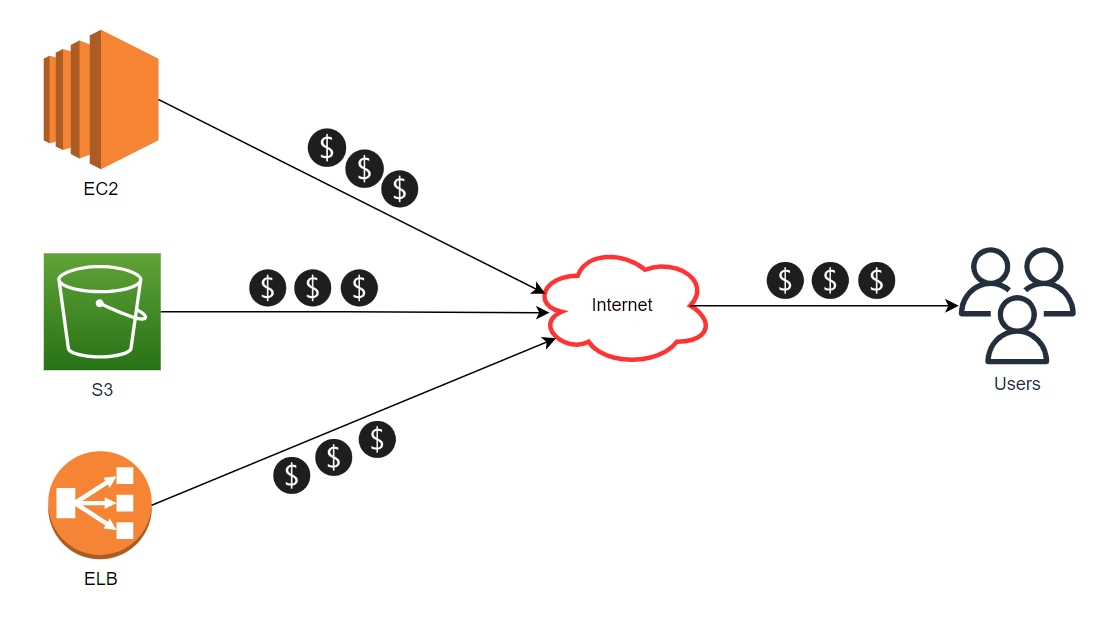
Plus, transferring data into CloudFront from other AWS resources (S3, EC2, API Gateway) is free of charge. By caching your content in CloudFront, you can significantly reduce expenses. The platform offers a free tier that provides customers with 1 TB of outbound data transfer and 10 million HTTP requests each month. Data transfer from CloudFront to the Internet is less expensive than standard data transfer rates.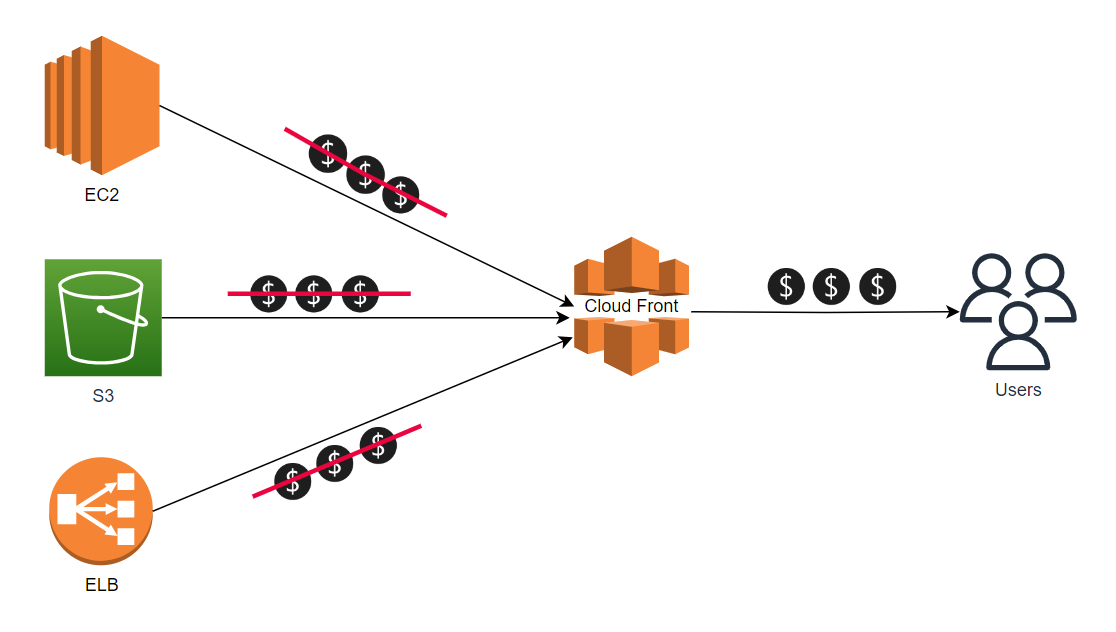
- Make full use of AWS pricing calculator:
To ensure a cost-effective deployment process, it is recommended to utilize the AWS pricing calculator beforehand. This involves a thorough analysis of various pricing options to strategically reduce expenses and align resource allocation with financial objectives. By taking this detailed approach, you can make informed decisions and optimize your deployment. - Abstain traffic over internet:
There are various methods that can be employed to eliminate charges that have been accrued over the internet, which are:- To establish private connectivity to AWS services within the same region without incurring data transfer fees is through VPC gateway endpoints.
- If you need to connect to services in different regions or services that do not support gateway endpoints, you may want to consider VPC interface endpoints. Although, it is important to note that VPC interface endpoints do have hourly service and data transfer charges.
- Whenever it is appropriate, AWS Direct Connect, a dedicated network connection between your network and AWS could be used to bypass the Internet.
Conclusion
By judiciously selecting AWS regions, leveraging replication strategies, and integrating services like Amazon CloudFront, organizations can minimize expenditure while maximizing performance and reliability. Additionally, utilizing private IP addresses, AWS pricing calculators, and alternative connectivity options such as VPC endpoints and AWS Direct Connect empowers businesses to align resource allocation with financial objectives. Embracing FinOps principles and proactive cost management strategies enables businesses to transform data transfer expenses into a strategic advantage, ensuring optimal utilization of cloud resources while maintaining fiscal responsibility in today's competitive digital environment.




